Resistance: The Consequence of Antibiotic Abuse
Antibiotic resistance is an increasing concern both in Nigeria and globally, and it's crucial to comprehend the impact of antibiotic misuse.
What is Antibiotic Resistance?
Antibiotic resistance arises when bacteria evolve to withstand the effects of antibiotics, rendering them ineffective in treating infections. This alarming phenomenon is a result of complex biological processes that allow certain bacteria to survive even in the presence of these powerful medications.
The development of resistance can occur through various mechanisms, including genetic mutations and the acquisition of resistance genes from other bacteria. Consequently, when antibiotics are overused or misused—such as when they are prescribed for viral infections, or when patients do not complete their prescribed courses—this creates an environment that favors the survival of resistant strains. As these resistant bacteria multiply and spread, they can cause infections that are significantly more difficult to treat, leading to prolonged illness, increased medical costs, and a higher risk of mortality.
Furthermore, the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria poses a serious public health threat, as it can compromise the effectiveness of standard medical procedures, such as surgeries and chemotherapy, which rely on antibiotics to prevent infections.
Addressing this critical issue requires a multifaceted approach that includes promoting responsible antibiotic use, enhancing infection prevention strategies, and investing in research to develop new antibiotics and alternative therapies. The global community must work collaboratively to combat the rise of antibiotic resistance to ensure that effective treatments remain available for future generations.
Effects of Misusing Antibiotics
1. Higher Mortality Rates: Infections that resist antibiotics can result in higher mortality rates, particularly in vulnerable groups like the elderly and young children.
2. Extended Illness: Resistant infections may cause longer hospitalizations, increased healthcare expenses, and extended illness duration.
3. Rising Healthcare Costs: The financial impact of antibiotic resistance is substantial, which requires spending more money on further tests and stronger, longer hospital stay and more expensive medications.
4. Limited Treatment Options: As antibiotics lose their effectiveness, the options for treating infections dwindle, complicating the ability of healthcare providers to treat patients successfully.
5. Higher Infection Risk: Antibiotic resistance elevates the risk of infections, especially in individuals with compromised and suppressed immune systems, such as those with chronic diseases or undergoing chemotherapy.
6. Challenge to Modern Medicine: Antibiotic resistance endangers the progress of modern medicine, including organ transplants, cancer therapies, and surgeries, which greatly depend on effective antibiotics.
Causes of Antibiotics Abuse
1. Overprescription: Healthcare professionals may overprescribe antibiotics, contributing to the development of resistance.
2. Self-Medication: Patients may self-medicate with antibiotics, leading to misuse and overuse. Examples of antibiotics that have been misused in Nigeria are Amoxiclav (Augmentin, Fleming etc.), Metronidazole (Flagyl), Cefuroxime (Zinnat) etc.
3. Lack of Education: Limited awareness about antibiotic resistance and proper use can contribute to abuse.
4. Agricultural Use: Antibiotics are often used in agriculture to promote growth and prevent disease, contributing to the development of resistance.
Prevention and Solutions
1. Responsible Prescribing: Healthcare professionals must prescribe antibiotics carefully, adhering to guidelines, ensuring the correct dosage for the appropriate duration, and only when essential.
2. Improved Education: Educating patients, healthcare professionals, and the general public about antibiotic resistance and proper use is crucial.
3. Antibiotic Stewardship: Establishing antibiotic stewardship initiatives in healthcare environments can assist in minimizing misuse and overuse.
4. Research and Development: Encouraging research and development of new antibiotics and alternative treatments is essential.
5. Cooperation: Both International and National cooperation, agreements and laws can help address the global issue of antibiotic resistance.
Written by Dr Popoola Faith, M.B.B.S., M.Med.All Categories
Recent Posts
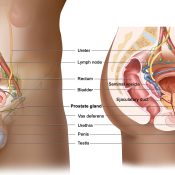
Prostate Cancer Screening
Resistance: The Consequence of Antibiotic Abuse
Support On The Go!
business@cubecover.ai