Prostate Cancer Screening
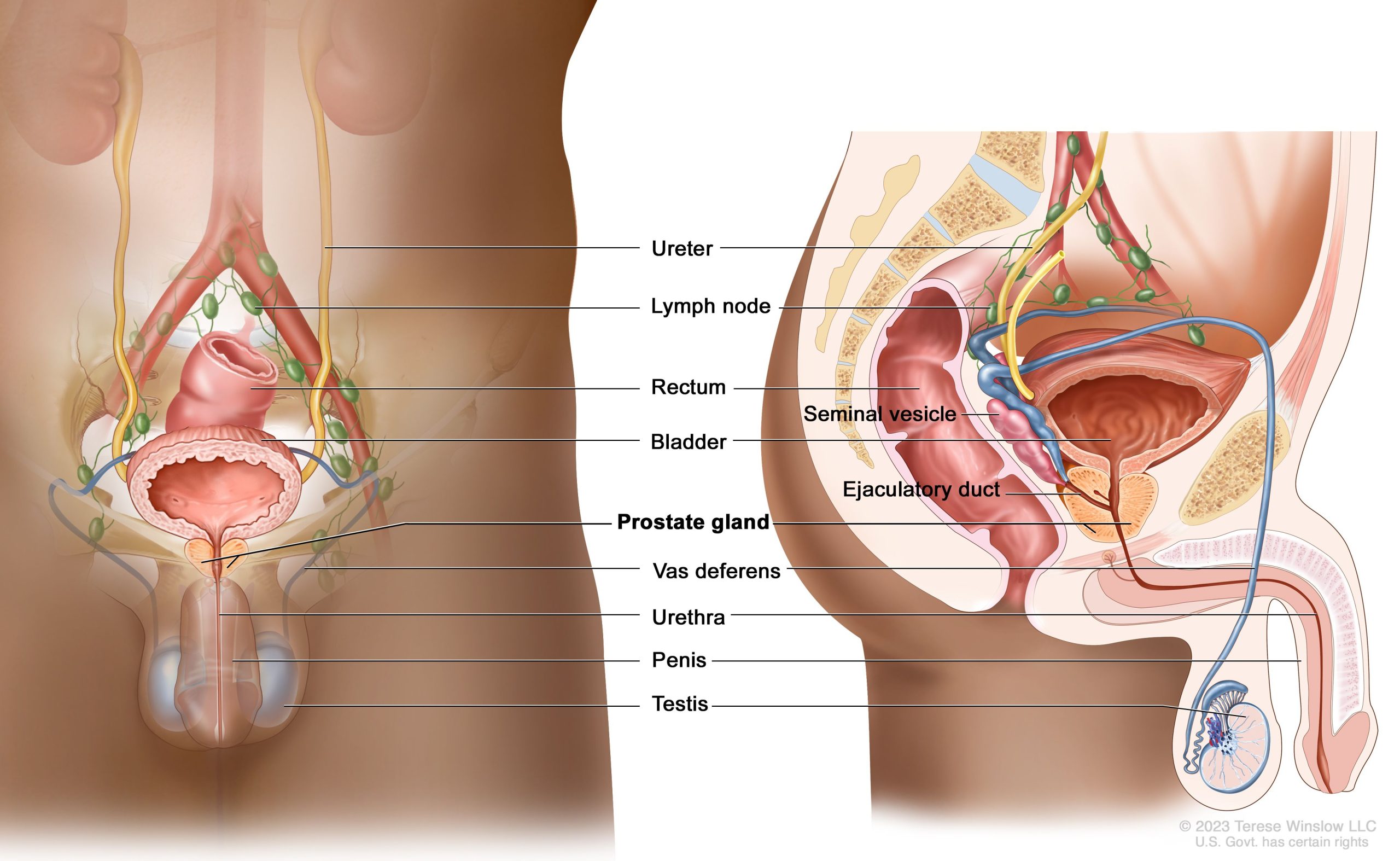
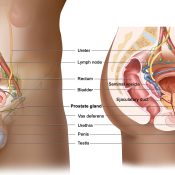
Prostate cancer is a malignant growth that develops in the prostate, a small gland resembling a walnut within the male reproductive system.
It generally progresses slowly and frequently shows no symptoms until reaching an advanced stage. Prostate cancer is more prevalent in older men.
Prostate cancer ranks among the most common cancers in men, and early detection is vital for effective treatment.
Screening for prostate cancer includes tests that can identify the disease before symptoms manifest. Here’s what you need to know about prostate cancer screening.
Why Screen for Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer typically develops gradually and might not present obvious symptoms in its initial phases. Screening is beneficial for early detection, making the cancer more manageable. Identifying it early can greatly enhance outcomes and boost the likelihood of effective treatment.
Who Should Get Screened?
Basically, all men with risk factors such as men between the ages of 55 to 70, men with a family history of prostate cancer and it`s safe to say any other kinds of cancers, men of African and African American ethnicity and other risks such as obesity, processed food diet, smoking and excessively use of alcohol.
Men with the above listed risked factors are advised to start screening from age 40.
Common Screening Tests
.
However, a rise in the PSA does not always mean the presence of malignancy, it could also be elevated in Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate) and Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (noncancerous enlargement of the prostate), therefore, further investigations must be done to reach a definite diagnosis.
.
Benefits of Screening
Screening can identify prostate cancer at an early stage, enhancing the effectiveness of treatment and potentially saving lives. Being aware of your PSA level allows your doctor to assess your risk and suggest suitable follow-up tests or treatments.
Possible Risks of Screening
Screening may occasionally result in false positives, suggesting the presence of cancer when there is none, which can cause undue stress and additional examinations. There are also issues of overdiagnosis and overtreatment, since certain prostate cancers develop so slowly that they might never pose any issues.
Making an Informed Decision
It's crucial to talk over the advantages and potential drawbacks of prostate cancer screening with your doctor. By doing so, you can jointly determine if screening is suitable for you, considering your age, risk factors, and individual preferences.
Conclusion
Screening for prostate cancer is an important method for early detection and better outcomes. By staying informed and consulting with your healthcare provider, you can make the most informed decision for your health and well-being.
.
Written by Dr Popoola Faith, M.B.B.S., M.Med.
.
All Categories
Recent Posts
Support On The Go!
business@cubecover.ai